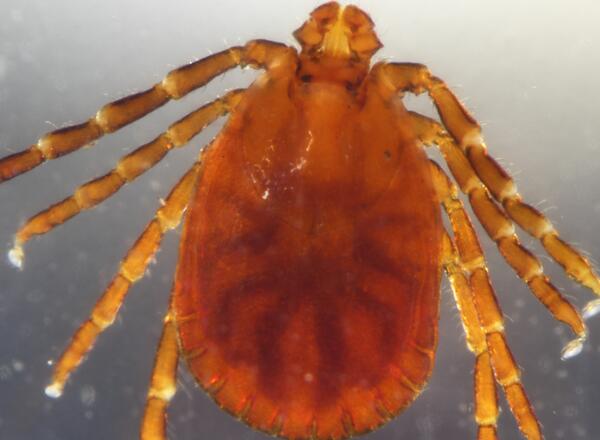

Asian Lonhorned Tick are light brown in color and are very small, often smaller than a sesame seed. They are difficult to detect because they are very small. The adult female is only about the size of a pea when it is full of blood (fully engorged).
Species found on
Thus far ALT has been found on numerous domesticated and wildlife species hosts including: sheep, goats, dogs, cats, horses, cattle, chickens, black bears, grey squirrels, red and grey foxes, groundhogs, striped skunks, white-tailed deer, elk, opossums, raccoons, Canada geese, barred owls, great horned owls, brown boobies, mice, blue jays, and red-tailed hawks (USDA, 2024).

Asian Longhorned Ticks (ALT) favors low-lying swampy areas, wooded areas, and taller grasses. Large numbers of ticks can be found in areas with established populations of ALT where these areas converge.
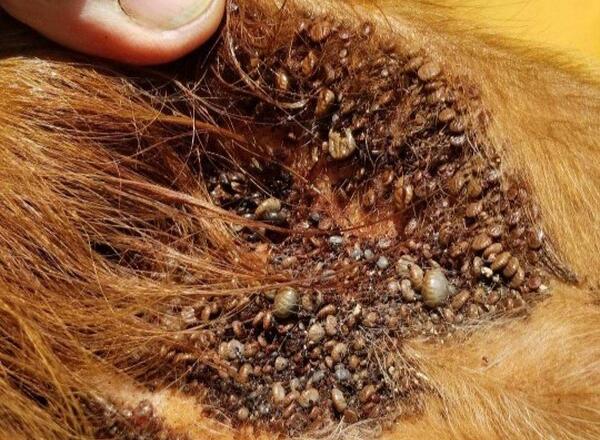
All stages of the life cycle of the tick can be present on a single animal at a given time. Ticks can be found on ears, brisket, udder, tail head/vulva areas, folds of skin; however, not all animals will be infested.
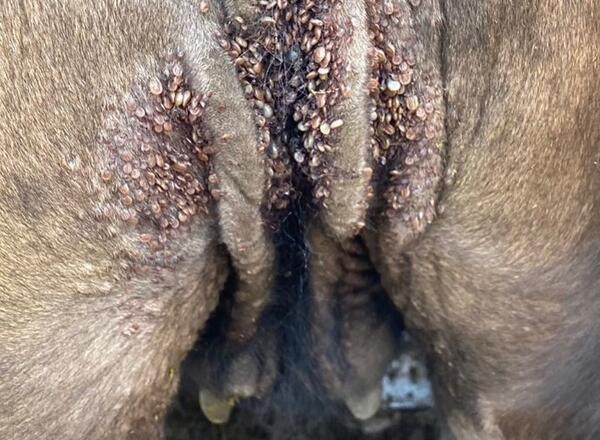
ALT appears to be susceptible to most of the chemical products commonly used to treat other species of ticks on cattle. If cattle continue to graze pastures that are heavily infested, they may become reinfected as drug levels provided by treatment drop off. The length of time that any of these products will keep cattle from becoming reinfected is not currently known but will likely vary based on the particular product and the number of ticks in the pasture.
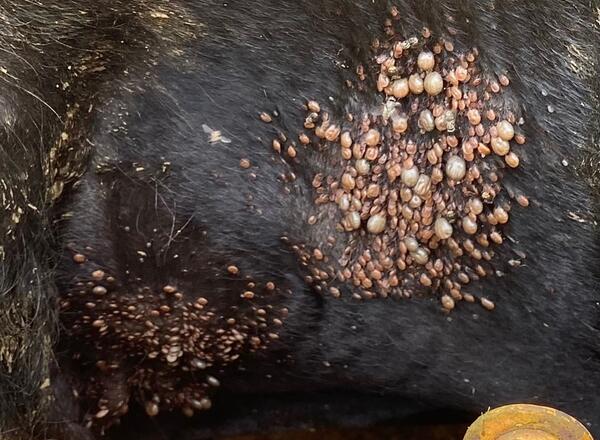
Mowing pastures will help keep ticks numbers lower than not mowing. Preliminary data suggests that the combination of mowing and chemical products can lessen tick burden on livestock. If Asian Longhorned Ticks are found in wooden areas, livestock should not roam the area until late fall when temperatures have fallen and ticks become inactive.
Consult your herd veterinarian to develop a plan for exctoparasite prevention.
If you suspect the Asian Longhorned Tick is on your farm
For more information
